Mathematics Class 10 NCERT Chapter - 2 FULL EXERCISE - 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 SOLUTIONS
CHAPTER 2
Polynomials Exercise Ex. 2.1
Solution 1
(ii) The graph of P(x) intersects the x-axis at only 1 point.
So, the number of zeroes is 1.
(iii) The graph of P(x) intersects the x-axis at 3 points.
So, the number of zeroes is 3.
(iv) The graph of P(x) intersects the x-axis at 2 points.
So, the number of zeroes is 2.
(v) The graph of P(x) intersects the x-axis at 4 points.
So, the number of zeroes is 4.
(vi) The graph of P(x) intersects the x-axis at 3 points.
So, the number of zeroes is 3.
Concept insight: Since the polynomial p(x) given here is a polynomial in variable x, so to find the number of zeroes, we look at the number of points where the graph intersects or touches the x-axis and not the y-axis.
At all these points where the graph intersects x axis the value of the polynomial y = p(x) will be zero.
Polynomials Exercise Ex. 2.2
Solution 1
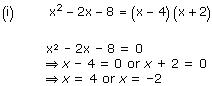
So, the zeroes of x² - 2x - 8 are 4 and -2.
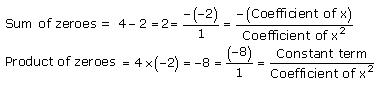
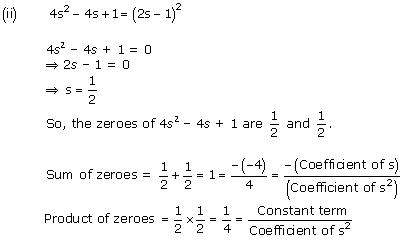
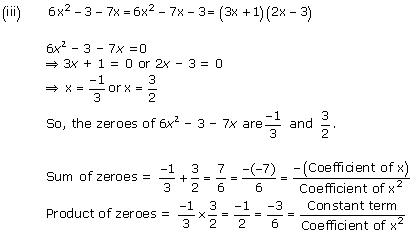
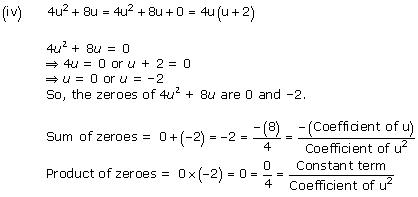
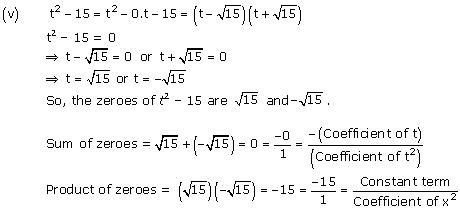
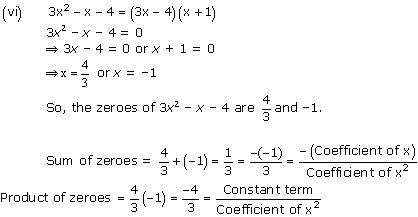
Concept insight: The zero of a polynomial is that value of the variable which when substituted in the polynomial makes its value 0.
When a quadratic polynomial is equated to 0, then the values of the variable obtained are the zeroes of that polynomial. The relationship between the zeroes of a quadratic polynomial with its coefficients is very important. Also, while verifying the above relationships, be careful about the signs of the coefficients.
Solution 2
(i) Let the required polynomial be ax² + bx + c, and let its zeroes ![]() and
and ![]()
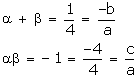
(ii) Let the polynomial be ax² + bx + c, and let its zeroes be

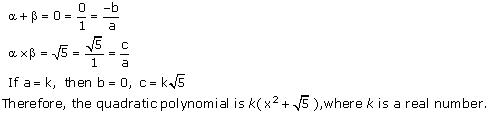
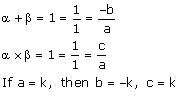
(v) Let the polynomial be ax² + bx + c, and its zeroes be
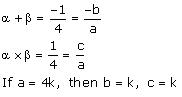
(vi) Let the polynomial be ax² + bx + c.
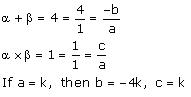
Concept insight: Since the sum and product of zeroes gives 2 relations between three unknowns so we assign a value to the variable a and obtain other values.
Alternatively If the sum and the product of the zeroes of a quadratic polynomial is given then polynomial is given by x2 - (sum of the roots)x + product of the roots, where k is a constant. And the simplest polynomial will be the one in which k = 1.
Polynomials Exercise Ex. 2.3
Solution 1

Quotient = x - 3
Remainder = 7x - 9

Quotient = x2 + x - 3
Remainder = 8
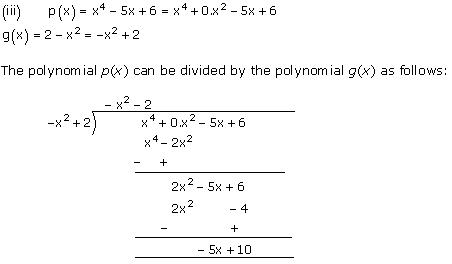
Quotient = -x2 - 2
Remainder = -5x + 10
Concept insight: While dividing one polynomial by another, first arrange the polynomial in descending powers of the variable. In the process of division, be careful about the signs of the coefficients of the terms of the polynomials. After performing division, one can check his/her answer obtained by the division algorithm which is as below:
Dividend = Divisor x Quotient + Remainder
Also, remember that the quotient obtained is a polynomial only.
Solution 2
(i) The polynomial 2t4 + 3t3 - 2t2 - 9t - 12 can be divided by the polynomial t2 - 3 = t2 + 0.t - 3 as follows:
Since the remainder is 0, t² - 3 is a factor of 2t4 + 3t3 - 2t2 - 9t - 12 .
(ii) The polynomial 3x4 + 5x3 - 7x2 + 2x + 2 can be divided by the polynomial x2 + 3x + 1 as follows:
Since the remainder is 0, x² + 3x + 1 is a factor of 3x4 + 5x3 - 7x2 + 2x + 2
(iii) The polynomial x5 - 4x3 + x2 + 3x + 1 can be divided by the polynomial x3 - 3x + 1 as follows:
Since the remainder is not equal to 0, x3 - 3x + 1 is not a factor of x5 - 4x3 + x2 + 3x + 1.
Concept insight: A polynomial g(x) is a factor of another polynomial p(x) if the remainder obtained on dividing p(x) by g(x) is zero and not just a constant. While changing the sign, make sure you do not change the sign of the terms which were not involved in the previous operation. For example in the first step of (iii), do not change the sign of 3x + 1.
Solution 3
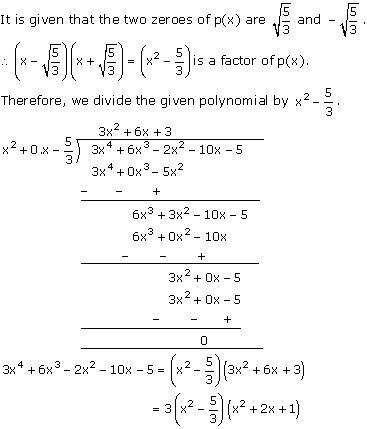
Now, x² + 2x + 1 = (x + 1)2
So, the two zeroes of x² + 2x + 1 are -1 and -1.
Concept insight: Remember that if (x - a) and (x - b) are factors of a polynomial, then (x - a)(x - b) will also be a factor of that polynomial. Also, if a is a zero of a polynomial p(x), where degree of p(x) is greater than 1, then (x - a) will be a factor of p(x), that is when p(x) is divided by (x - a), then the remainder obtained will be 0 and the quotient will be a factor of the polynomial p(x). To cross check your answer number of zeroes of the polynomial will be less than or equal to the degree of the polynomial.
Solution 4
Quotient = (x - 2)
Remainder = (-2x + 4)
Let g(x) be the divisor.
According to the division algorithm,
Dividend = Divisor x Quotient + Remainder
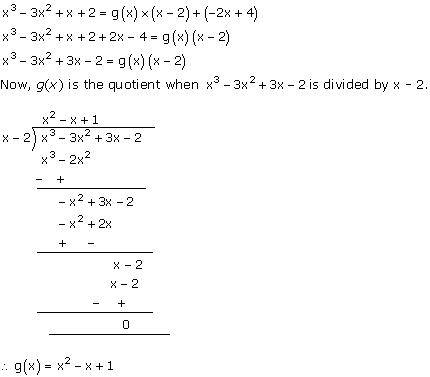
Concept insight: When a polynomial is divided by any other non-zero polynomial, then it satisfies the division algorithm which is as below:
Dividend = Divisor x Quotient + Remainder
Divisor x Quotient = Dividend - Remainder
So, from this relation, the divisor can be obtained by dividing the result of (Dividend - Remainder) by the quotient.
Solution 5
p(x) = g(x) x q(x) + r(x), where r(x) = 0 or degree of r(x) < degree of g(x).
(i) Degree of quotient will be equal to degree of dividend when divisor is constant.
Let us consider the division of 18x2 + 3x + 9 by 3.
Here, p(x) = 18x2 + 3x + 9 and g(x) = 3
q(x) = 6x2 + x + 3 and r(x) = 0
Here, degree of p(x) and q(x) is the same which is 2.
Checking:
p(x) = g(x) x q(x) + r(x)
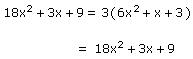
Thus, the division algorithm is satisfied.
(ii) Let us consider the division of 2x4 + 2x by 2x3,
Here, p(x) = 2x4 + 2x and g(x) = 2x3
q(x) = x and r(x) = 2x
Clearly, the degree of q(x) and r(x) is the same which is 1.
Checking,
p(x) = g(x) x q(x) + r(x)
2x4 + 2x = (2x3 ) x x + 2x
2x4 + 2x = 2x4 + 2x
Thus, the division algorithm is satisfied.
(iii) Degree of remainder will be 0 when remainder obtained on division is a constant.
Let us consider the division of 10x3 + 3 by 5x2.
Here, p(x) = 10x3 + 3 and g(x) = 5x2
q(x) = 2x and r(x) = 3
Clearly, the degree of r(x) is 0.
Checking:
p(x) = g(x) x q(x) + r(x)
10x3 + 3 = (5x2 ) x 2x + 3
10x3 + 3 = 10x3 + 3
Thus, the division algorithm is satisfied.
Concept insight: In order to answer such type of questions, one should remember the division algorithm. Also, remember the condition on the remainder polynomial r(x). The polynomial r(x) is either 0 or its degree is strictly less than g(x). The answer may not be unique in all the cases because there can be multiple polynomials which satisfies the given conditions.
Polynomials Exercise Ex. 2.4
Solution 1
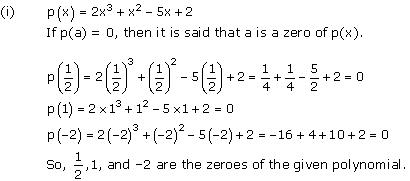
On comparing the given polynomial with the polynomial ax3 + bx2 + cx + d, we obtain a = 2, b = 1, c = -5, d = 2
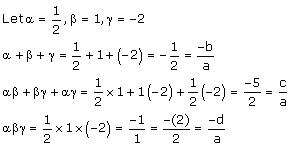
Thus, the relationship between the zeroes and the coefficients is verified.
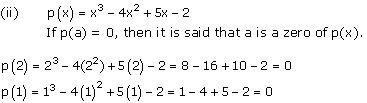
On comparing the given polynomial with the polynomial ax3 + bx2 + cx + d, we obtain a = 1, b = -4, c = 5, d = -2.
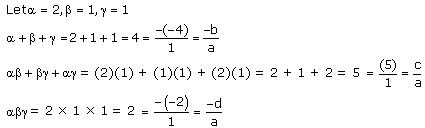
Thus, the relationship between the zeroes and the coefficients is verified.
Concept insight: The zero of a polynomial is that value of the variable which makes the polynomial 0. Remember that there are three relationships between the zeroes of a cubic polynomial and its coefficients which involve the sum of zeroes, product of all zeroes and the product of zeroes taken two at a time.
Solution 2
According to the given information:
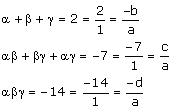
If a = k, then b = -2k, c = -7k, d = 14k
Thus, the required cubic polynomial is k(x3 - 2x2 - 7x + 14), where k is any real number.
The simplest polynomial will be obtained by taking k = 1.
Concept insight: A cubic polynomial involves four unknowns and we have three relations involving these unknowns, so the coefficients of the cubic polynomial can be found by assuming the value of one unknown and then finding the other three unknowns from the three relations.
Solution 3
The zeroes of the polynomial p(x) are given as a - b, a, a + b.
Comparing the given polynomial with dx3 + ex2 + fx + g, we can observe that
d = 1, e = -3, f = 1, g = 1
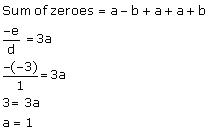
Therefore, the zeroes of p(x) are 1-b, 1, 1+b .
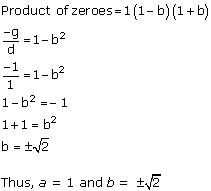
Concept insight: When the polynomial and its zeroes are given then, remember to apply relationships between the zeroes and coefficients .
These relations involve the sum of the zeroes, product of zeroes and the product of zeroes taken two at a time.
Solution 4
Therefore, x2 - 4x + 1 is a factor of the given polynomial.
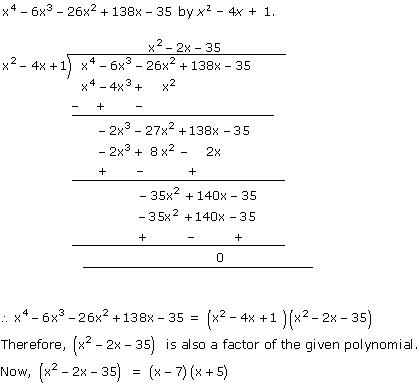
Hence, 7 and -5 are also zeroes of the given polynomial.
Concept insight: If a is a zero of a polynomial p(x), where degree of p(x) is greater than 1, then (x - a) will be a factor of p(x) that is when p(x) is divided by (x - a), then the remainder obtained will be 0 and the quotient will be a factor of p(x) using division algorithm. Remember that if (x - a) and (x - b) are factors of a polynomial, then (x - a)(x - b) will also be a factor of that polynomial.
Solution 5
Dividend = Divisor x Quotient + Remainder
Divisor x Quotient = Dividend - Remainder
It will be perfectly divisible by x2 - 2x + k.
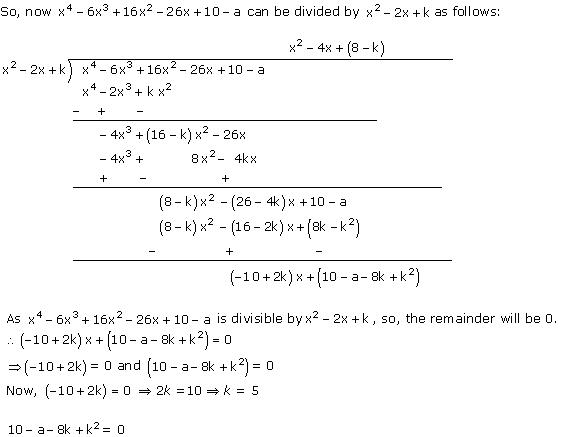
10 - a - 8 x 5 + 25 = 0
10 - a - 40 + 25 = 0
- 5 - a = 0
a = -5
Thus, k = 5 and a = -5.
Concept insight: When a polynomial is divided by any non-zero polynomial, then it satisfies the division algorithm which is as below:
Dividend = Divisor x Quotient + Remainder
Divisor x Quotient = Dividend - Remainder
So, from this relation, it can be said that the result (Dividend - Remainder) will be completely divisible by the divisor.

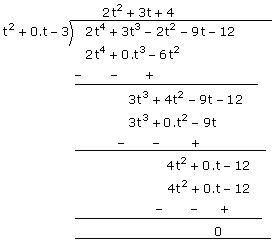
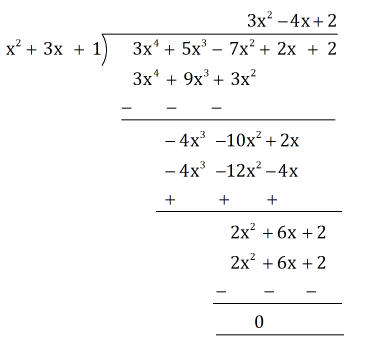
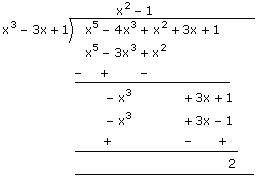




No comments